5G network deployment services transforming connectivity
5G network deployment services sets the stage for a technological revolution, reshaping how we connect and communicate in an increasingly digital world. With its ability to deliver lightning-fast speeds and significantly lower latency, 5G technology is not just an upgrade; it’s a game-changer that impacts diverse sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities. This advancement paves the way for innovation, enhancing efficiency and enabling new applications that were once thought impossible.
As we delve into the intricacies of 5G deployment, we will explore the importance of this technology, the challenges faced during its rollout, and successful strategies that pave the way for a seamless transition to this next-generation network. From understanding the essential components required for deployment to examining global case studies, the future of connectivity is bright and full of potential.
Importance of 5G Network Deployment Services
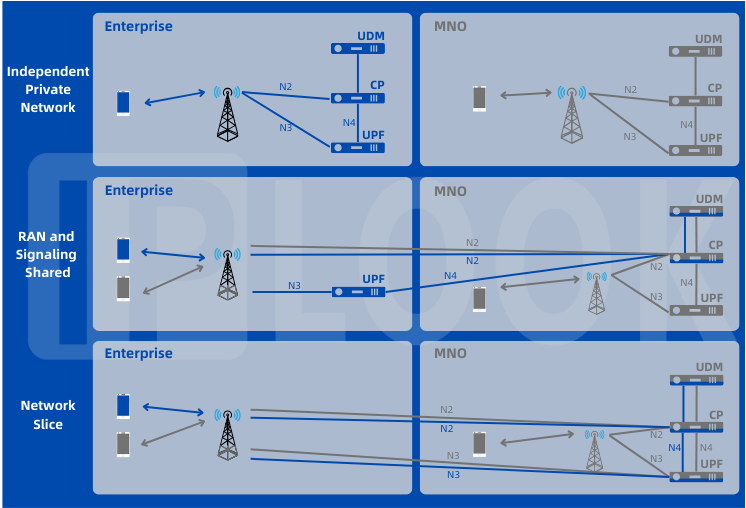
The deployment of 5G networks marks a significant milestone in modern telecommunications, transforming how data is transmitted and utilized across various sectors. With its ultra-fast speeds and reduced latency, 5G enables a new wave of innovation and connectivity that is essential for today’s digital landscape.The significance of 5G lies in its capability to enhance communication infrastructure, allowing for a seamless connection between devices and systems.
This technology not only improves user experience but also fosters advancements in numerous industries. Faster network speeds and lower latency enable real-time data analysis and communication, which is crucial for applications like remote surgery in healthcare, precision manufacturing in industrial settings, and the interconnected frameworks of smart cities.
Impact of 5G on Key Industries
G deployment significantly influences various industries, creating opportunities and challenges that reshape their operational frameworks. The following points Artikel its impact across critical sectors:
- Healthcare: 5G facilitates telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, allowing healthcare professionals to provide care from any location. This technology enables high-definition video consultations and real-time health data transmission, improving patient outcomes.
- Manufacturing: The integration of 5G in manufacturing leads to smart factories where machines communicate and operate with minimal human intervention. This connectivity enhances productivity through automation, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization.
- Smart Cities: 5G underpins the development of smart cities, enabling intelligent transportation systems, efficient energy management, and enhanced public safety services. Through interconnected devices, cities can monitor traffic patterns in real-time, manage resources effectively, and improve the quality of urban life.
The deployment of 5G is not just about speed; it fundamentally alters the framework within which industries operate, making them more efficient, responsive, and capable of leveraging advanced technologies like AI and IoT.
5G is the backbone of the digital economy, driving innovation and enabling a connected world.
Challenges in 5G Network Deployment
Deploying a robust and efficient 5G network is not without its challenges. As telecommunications companies strive to deliver faster speeds and more reliable connections, they confront various obstacles at multiple stages of deployment. Understanding these challenges is crucial for stakeholders aiming for successful implementation.Regulatory and infrastructural challenges play a significant role in the deployment of 5G networks. As this technology advances, it often outpaces existing regulations, leading to potential legal and compliance issues.
Additionally, the need for new infrastructure can create hurdles, particularly in urban areas where existing frameworks may not support the installation of new technologies.
Regulatory Challenges
The regulatory environment surrounding 5G deployment can be complex and cumbersome. Different countries and regions have varying regulatory frameworks that can affect deployment timelines. Some of the key regulatory challenges include:
- Licensing and Spectrum Allocation: Securing the necessary licenses to operate on specific frequencies can be a lengthy and competitive process.
- Compliance with Local Laws: Regulations regarding zoning, environmental impact, and public safety can delay installation efforts.
- Coordination with Government Entities: Engaging with various governmental agencies for approvals and permits can lead to bureaucratic delays.
The infrastructural aspect is equally critical as it directly impacts the physical deployment of 5G technology.
Infrastructural Challenges
Infrastructural challenges refer to the physical limitations encountered during the deployment of 5G networks. These challenges can impede the pace of rollout and affect overall network performance. Some notable infrastructural challenges include:
- Existing Infrastructure Limitations: Many areas were built with older technologies that may not support the upgrade paths necessary for 5G.
- Site Acquisition Issues: Finding suitable locations for new cell towers or small cells can be difficult, especially in densely populated urban environments.
- Backhaul Connectivity: Ensuring high capacity and low-latency backhaul connections to support 5G traffic can be challenging, particularly in rural areas.
Technical Issues
Technical issues can arise during the installation and implementation phases of 5G networks, influencing their overall effectiveness and reliability. These technical challenges encompass a range of operational difficulties, including:
- Integration with Existing Networks: Seamlessly integrating 5G technology with existing 4G and legacy systems can present complex technical difficulties.
- Equipment Compatibility: Ensuring that all installed hardware and software work together efficiently is crucial for optimal performance.
- Network Configuration: Configuring the network correctly to handle increased load and diverse applications requires careful planning and execution.
Mitigating these challenges through comprehensive planning and collaboration among stakeholders is essential for successful 5G deployment.
Components of 5G Network Deployment Services

The deployment of a 5G network is a complex task that requires a variety of components to ensure optimal performance and coverage. As the fifth generation of mobile networks, 5G introduces advanced capabilities that necessitate specific hardware and software components. Understanding these elements is crucial for organizations looking to implement 5G technology effectively.The successful deployment of a 5G network involves a combination of both hardware and software components that work together to deliver high-speed connectivity and low-latency communication.
Each component plays a vital role in the overall infrastructure, ensuring that the network can handle increased data traffic and provide reliable service.
Essential Components for 5G Deployment
Several essential components are necessary for a robust and efficient 5G network deployment. Each of these components has a distinct function that contributes to the network’s overall capabilities.
- Base Stations: The backbone of the 5G network, these stations transmit and receive signals to and from user devices. They are designed to handle higher frequencies and provide extensive coverage.
- Small Cells: These are low-power base stations that cover smaller areas, enhancing capacity and coverage, especially in urban environments with high user density.
- Core Network: The core network is responsible for data routing and management. It integrates various elements such as data storage, processing, and service delivery.
- antennas: Advanced antennas, such as Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), are crucial for maximizing data throughput and improving signal reliability.
- Network Slicing: This technology allows multiple virtual networks to be created on a single physical infrastructure, enabling tailored services for different applications and industries.
- Edge Computing: By processing data closer to the end user, edge computing reduces latency and enhances real-time data processing capabilities.
- Transport Network: This includes fiber optic cables and microwave links that connect base stations to the core network, ensuring fast and reliable data transfer.
Role of Hardware and Software in Deployment
In 5G deployment, hardware and software work in tandem to create a seamless experience for end users. The hardware components, such as routers, switches, and antennas, provide the physical infrastructure necessary for data transmission. Conversely, software components, including network management systems and analytics tools, play a critical role in monitoring network performance, optimizing traffic flow, and ensuring efficient resource allocation.The integration of software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV) enhances flexibility and scalability in 5G networks.
This allows service providers to dynamically manage network resources and quickly adapt to changing demands or conditions.
Importance of Site Acquisition and Preparation
Site acquisition and preparation are crucial steps in the 5G deployment process. Selecting the right locations for base stations and small cells directly impacts network performance and coverage. The process involves identifying potential sites, obtaining necessary permits, and ensuring compliance with local regulations.Proper site preparation includes evaluating the physical environment, such as assessing the structural integrity of buildings for rooftop installations and ensuring that the locations have adequate power supply and backhaul connectivity.
The phrase
“The success of a 5G deployment hinges on meticulous site selection and preparation.”
underscores the importance of these preliminary steps. A well-planned site acquisition strategy not only expedites the deployment process, but also minimizes operational challenges, leading to a more efficient rollout of the 5G network.
Strategies for Successful 5G Deployment
The deployment of 5G networks involves intricate planning and collaboration among various stakeholders. As telecommunications companies and service providers embark on this ambitious journey, implementing effective strategies becomes crucial for ensuring a successful rollout. This section Artikels key methods for planning a 5G deployment project, coordinating with local authorities, and managing associated risks.
Planning a 5G Deployment Project
A detailed planning process is fundamental for the successful deployment of a 5G network. This involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses several critical aspects.
1. Conduct a Market Analysis
Understanding the target market’s needs and existing infrastructure is essential. This includes assessing the demand for 5G services and identifying potential competitors in the area.
2. Define Objectives and Scope
Clearly outlining the project’s goals, such as coverage areas, expected user capacity, and service quality, helps in aligning resources effectively.
3. Develop a Detailed Timeline
Establishing a realistic timeline that includes all phases of deployment, from site acquisition to network testing, allows for better resource allocation and tracking of progress.
4. Select Technology Partners
Collaborating with technology vendors and equipment suppliers is crucial. Ensuring that partners have experience in 5G technologies will facilitate smoother implementations.
5. Budgeting and Financing
Developing an accurate budget that includes funding sources, such as investments, loans, and anticipated revenue streams, is crucial for mitigating financial risks.
Coordinating with Local Authorities and Stakeholders
Effective communication and coordination with local authorities and stakeholders play a pivotal role in the deployment process. This involves several steps to ensure a smooth collaboration.
1. Engage Early
Initiating discussions with local governments and regulatory bodies early in the planning process can help identify potential regulatory hurdles and obtain necessary permits.
2. Public Outreach
Organizing community engagement programs to inform residents about the benefits of 5G technology can help address any public concerns and build support.
3. Establish Partnerships
Collaborating with local businesses, municipalities, and other stakeholders can facilitate access to sites and resources, enhancing the deployment process.
4. Monitor Compliance
Regularly updating authorities on project progress and ensuring compliance with local regulations can foster a positive relationship and aid in obtaining approvals.
Risk Management Strategies for 5G Deployment
Risk management is a critical component of any 5G deployment strategy. Identifying potential risks and implementing mitigation strategies can safeguard the project from unforeseen challenges.
1. Identify Risks
Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential issues, including technological, operational, financial, and regulatory risks.
2. Develop Mitigation Plans
For each identified risk, develop a mitigation plan outlining actionable steps to reduce the impact or likelihood of the risk occurring.
3. Continuously Monitor Risks
Establish a risk monitoring process that allows for the ongoing assessment of potential risks throughout the deployment phase.
4. Contingency Planning
Prepare contingency plans for high-impact risks, ensuring that the project can adapt quickly to unexpected challenges.
5. Stakeholder Involvement
Involving stakeholders in the risk management process ensures diverse perspectives are considered, enhancing the strategy’s effectiveness.
Effective planning, coordination, and risk management are essential to achieving a successful 5G deployment that meets the needs of users and stakeholders alike.
Case Studies of 5G Network Deployment

The deployment of 5G networks has been a transformative journey for many countries and companies around the globe. As this next-generation technology rolls out, numerous case studies highlight successful implementations that offer valuable lessons. These deployments showcase innovative strategies, unique challenges, and the varying pace of adoption across different regions.
Successful Global Deployments of 5G
Several countries have achieved significant milestones in their 5G deployment efforts, each with unique strategies and outcomes. Here are a few noteworthy examples:
- South Korea: South Korea led the way in 5G adoption, launching its commercial 5G services in April 2019. The country’s strategy involved a close collaboration between major telecom operators and the government. By aggressively investing in infrastructure, South Korea was able to cover urban areas swiftly, with over 85% of the population having access to 5G within a year of the launch.
This rapid deployment has driven advancements in smart city applications, augmented reality, and telemedicine.
- United States: The U.S. has seen a fragmented but robust rollout of 5G, with major players like Verizon and AT&T deploying their networks in varying frequencies. Verizon’s strategy focused on millimeter-wave technology, resulting in ultra-fast speeds but limited range. In contrast, AT&T utilized a lower-band spectrum, which offered broader coverage at slower speeds. This divergence highlights the importance of tailoring deployment strategies to specific market needs and geographic challenges.
- China: China’s approach to 5G deployment has been characterized by a vast and state-driven initiative. The country launched its commercial 5G services in November 2019, supported by significant public investment. By the end of 2020, China had installed over 700,000 5G base stations, focusing on dense urban areas and key industries. This nationwide effort not only promotes 5G access but also fuels domestic innovation in sectors such as manufacturing and transportation.
- United Kingdom: The UK’s deployment has been marked by partnerships with tech companies and a push for rural connectivity. While initially slower in rollout compared to other countries, the UK has made strides by leveraging existing infrastructures, such as utilizing street furniture for 5G antennas. This approach has provided a cost-effective solution for expanding coverage in underserved areas.
Lessons Learned from 5G Deployment Projects
Several key lessons can be derived from the diverse approaches taken by various nations and companies in the deployment of 5G networks:
- Collaboration is Key: Successful deployments often require cooperation between government entities, private companies, and stakeholders. For instance, the partnership model in South Korea accelerated the rollout and enhanced service offerings.
- Infrastructure Investment: Significant investment in infrastructure is essential for a successful 5G rollout. China’s massive public investment underscores the role of government support in facilitating widespread access.
- Technology Choices Matter: The choices of frequency bands and technology (e.g., millimeter-wave vs. sub-6 GHz) can significantly affect coverage and speed. The U.S. experience shows the trade-offs between high speeds and broad coverage.
- User-Centric Approach: Understanding user needs and preferences is critical. In the UK, the focus on rural connectivity demonstrates the necessity of catering to diverse demographics.
Comparative Analysis of Different Deployment Strategies
The strategies employed in 5G deployment vary significantly across different regions, influenced by factors such as existing infrastructure, regulatory environments, and market dynamics. Here’s a comparison of several notable strategies:
| Country/Region | Deployment Strategy | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| South Korea | Rapid urban rollout | Smart cities, IoT, and AR applications |
| United States | Fragmented market with varied technologies | Speed vs. coverage balance, competitive differentiation |
| China | State-driven, large-scale infrastructure investment | Industry innovation, nationwide coverage |
| United Kingdom | Partnerships for cost-effective solutions | Addressing rural connectivity and existing infrastructure |
“The success of 5G deployment isn’t merely about technology; it’s equally about strategy, investment, and collaboration across sectors.”
Future of 5G Network Deployment Services
The future of 5G network deployment services promises to be dynamic and transformative, as the technology continues to evolve and adapt to the ever-changing demands of users and industries. As we look ahead, it’s essential to understand the emerging trends, anticipated advancements, and the potential evolution toward 6G and beyond.
Emerging Trends in 5G Technology, 5G network deployment services
Several emerging trends are shaping the landscape of 5G network deployment services. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into network management is revolutionizing how networks are optimized and maintained. These technologies enable predictive maintenance and real-time analytics, improving service reliability and user satisfaction.Another trend is the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT), which relies heavily on 5G infrastructure.
The expansion of connected devices will lead to a surge in data traffic, necessitating more robust and scalable solutions. Additionally, edge computing is becoming more prominent, allowing data processing to occur closer to the source, reducing latency and improving application performance.
Anticipated Advancements in Infrastructure
Future advancements in 5G infrastructure are expected to enhance network capabilities significantly. One key area of development is the deployment of small cell technology, which will support dense urban areas and improve coverage. This technology allows service providers to install small, low-power nodes that enhance signal strength and capacity without the need for large cell towers.Moreover, advancements in fiber optic technology, such as the deployment of dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM), will facilitate faster and more reliable data transmission.
This increase in bandwidth will support the high data rates required for applications like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and ultra-high-definition video streaming.
“The future of connectivity lies in seamless integration across various technology platforms, driving innovation in communication and user experience.”
Potential Evolution of 6G and Beyond
Looking beyond 5G, the potential evolution to 6G technology is already being discussed among researchers and industry experts. 6G is anticipated to support data rates exceeding 100 Gbps, significantly surpassing the capabilities of 5G. This evolution will be driven by advancements in terahertz (THz) communication technologies, which promise to enhance wireless capacity and performance.In terms of applications, 6G may facilitate new use cases such as holographic communication and brain-computer interfaces, dramatically transforming the way individuals and businesses interact with technology.
Furthermore, the integration of satellite networks with terrestrial networks could enhance global connectivity, especially in underserved regions.As we prepare for these advancements, the collaboration between telecommunications companies, technology providers, and regulatory bodies will play a crucial role in shaping the future of 5G and beyond. The drive for innovation will not only enhance existing services but also unlock new opportunities for economic growth and societal advancement.
User Queries: 5G Network Deployment Services
What are the key benefits of 5G network deployment services?
The key benefits include faster data speeds, lower latency, improved connectivity for IoT devices, and enhanced support for advanced applications like telemedicine and autonomous vehicles.
How long does it typically take to deploy a 5G network?
Deployment timelines vary based on location and infrastructure but can range from several months to a few years, depending on regulatory and technical factors.
What are the main challenges faced during deployment?
Challenges include regulatory hurdles, high infrastructure costs, coordination with local authorities, and technical issues related to existing networks.
How can businesses prepare for the transition to 5G?
Businesses can prepare by investing in compatible technology, staying informed about industry trends, and collaborating with network providers for an efficient transition.
What is the expected impact of 5G on industries?
5G is expected to revolutionize industries by enabling real-time data processing, improving operational efficiency, and creating opportunities for new services and applications.